Introduction to Condensers
● It is an important device used in the high pressure side of the refrigeration system.
● It's function is to de-superheater and condenser the refrigerant vapour from the discharge of the compressor.
● First heat is transferred to the wall of the condenser tube by conduction and then from condenser tube to the condensing or cooling medium by convection. The cooling medium may be air, water or combination of two.
Classification of Condenser:
The condenser are mainly classified into three main types:
(1) Air cooled condenser - use air as the cooling media.
(2) Water cooled condenser - use water as a condensing media.
(3) Evaporative condenser use both air and water as condensing
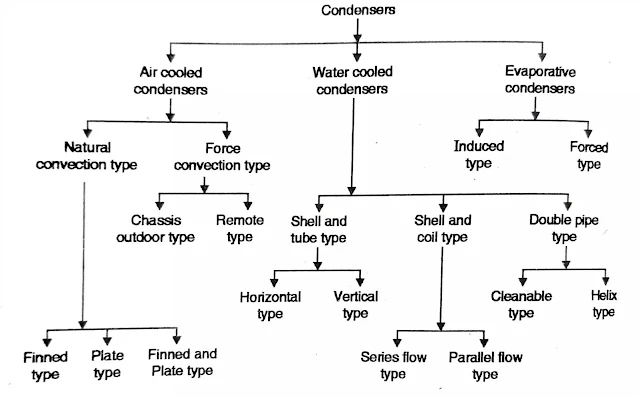
Air Cooled Condenser:
● The condenser is usually made of copper or steel tubing with fins attached which assist in rapid heat transfer. Size o tube ranges from 6 to 18 mm. outside diameter depends upon the size of condenser.
● The refrigerant flows inside the tubes and air flow is circulated outside.
● These condensers are preferred for small capacity refrigeration or air-conditioning system. Generally copper tubes because of excellent heat transfer ability.
● The steel tube condenser used for Ammonia refrigeration system.
● The fins are made of aluminium because of light in weight.
● The disadvantage of this condenser is that it operates at a higher condensing temperature than a water cooled condenser.
● Higher condensing temperature causes the compressor to work more.
Type of Air Cooled Condenser:
1. Natural Convection Air Cooled Condenser:
● In this the heat transfer from the condenser coil to the air by natural convection.
● As air comes in contact with the warm condenser tube, it absorbs heat from the refrigerant and thus temperature of air increase. So the density of air is decreased and rises up and the cold atmospheric air from bottom moves upward to absorb the heat from the condenser.
● The heat transfer rate is slower therefore required large surface area compared to force convection condenser. These are used for small capacity plant as domestic refrigerator, water cooler, etc.
2. Forced Convection Air Cooled Condenser:
● In this type fan is used to force the air the coil to increase heat transfer rate.
These are of two types:
(a) Base mounted air-cooled type.
(b) Remote air-cooled type.
Water Cooled Condenser:
● In this water is used as cooling medium.
● The condensing temperature of these condensers are 5 to 15°C above the temperature of entering water. These are always preferred where adequate supply of clear inexpensive water and waste disposal facilities available. These are suitable for large capacity refrigerator plant.
These are of following two types:
(1) Waste water system
(2) Recirculated water system
(1) Waste water system :
In this system water is taken from the main water supply and is disposed off in a sewer, after it does its work in condenser. This system is suitable when quantity of water is cheaply available and it disposed easily.
(2) Recirculated water system :
After condensation, this water is send to cooling water where it again cooled and this cooling water again recycled for condensation of refrigerant.
Types of Water Cooled Condenser:
The water cooled condenser again classified into:
1. Shell and Tube Condenser
2. Shell and Coil Condenser
3. A Double Pipe Condenser (Tube-In-Tube)
(a) Counter flow tube in tube condenser
(b) Parallel tow tube in tube condenser
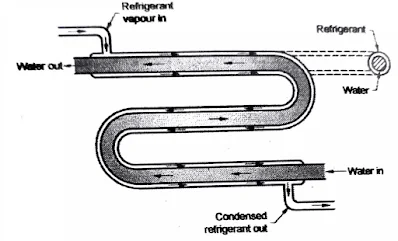
1. Shell and Tube Condenser:
● The shell and tube condenser consist of shell, tube sheets and tubes, water boxes and refrigerant connection. In the smaller size the shell may be standard pipe but welded shell are used for larger size.
● Two pass horizontal shell and tube condenser is equipped with enclosed water box and mounted in horizontal position.
● The tube sheet usually 1 inch thick are welded to the shell and drilled to receive tube.
● The tubes are inserted through their respective tube sheet hole and welded to provide gas tight joint.
● The refrigerant vapour from the compressor enters the top of the condenser and around the tube while the cooling water flows through the tube.
● The vapour gets condensed as it comes in contact with the water tubes by rejecting heat to flowing water. These condensate flows bottom of the shell.
● The liquid refrigerant from condenser flow directly to an expansion valve.
Disadvantages of horizontal shell and tube condenser:
(1) They must be taken out of service for cleaning.
(2) Water pumping, friction head may be high.
(3) Frequent cleaning may be needed to maintain efficiency because of smaller tube.
(4) Pump work increase power required to circulate the water.
Application :
(1) It is used in cold storage boxes and freezers.
(2) These are used in chemical and food processing industries.
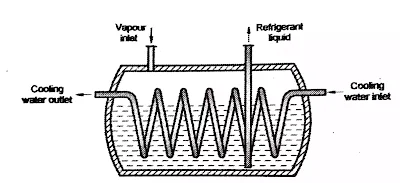
2. Shell and Coil Condenser:
● It uses a helical water coil in the shell instead of straight tube and a welded-steel shell.
● The connection for taking out condensed liquid refrigerant is so made that it dips in the liquid refrigerant at the bottom position which acts as a receiver.
● The refrigerant vapour from the compressor enter from top of the shell. As vapour comes in contact with coil it condensed.
● As condenser is fitted on high pressure side and the evaporator on low pressure side.
● The liquid refrigerant flow to expansion valve by siphon (high pressure to low pressure) so no need of extra receiver. Since the tube is in the form of coil, the water side of the tube is difficult to brushed but can be cleaned only by chemically.
3. A Double Pipe Condenser : (Tube-in-Tube) :
● It consists of concentric tubes with refrigerant condensing in the annular space and the water flowing the inner pipe. This is popular because it can be easily made to fit the size of the unit to be cooled.
● The outside tube is also cooled by surrounding air providing an efficient operation.
● Heat transfer rates are low in this type of condenser if the tubes are long because the poor drainage of the condensing refrigerant keeps the vapour from coming in contact with water tube.
● These are of two types:
(a) Counter flow tube in tube condenser:
In this type, cooling water flow from the bottom side and flow in opposite direction of refrigerant flow which enter from top side.
(b) Parallel flow tube in tube condenser:
● In this the cooling water and refrigerant vapour flow in same direction.
● Counter flow condenser are preferred because it gives high heat transfer rate since cold water is used to final cooling of the liquid refrigerant and warmest water absorbs heat from the hottest vapour, therefore the temperature difference between water and refrigerant remains fairly constant throughout the condenser.
● In parallel flow, the temperature difference between them increase the ability of water to absorb heat decrease as it passes through the condenser.
Disadvantages :
(1) In this large number of joints and connections needs in large installation increase chance of leakage.
(2) These are difficult to clean and do not provide enough space for separation of vapour and water. For this reasons are not much used in large installation, but they must be cleaned chemically.
(3) In case of a leak, the entire unit must be replaced.
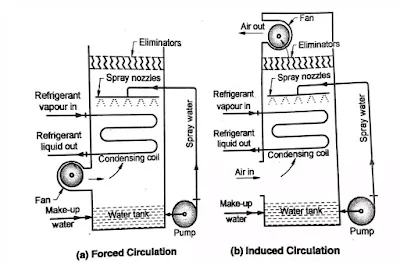
Evaporative Condenser:
● An evaporative condenser combines the functions of a cooling tower and condenser. It is of two types forced circulation type and induced circulation type.
● It consists of a casing enclosing a fan or blower, water eliminator, refrigerant condensing coil, water, tank, float valve and a spray pump outside the casing.
● The spray pump circulate the water from water tank at the bottom of the unit to the spray nozzle over the refrigerant coil.
● The fan pull or forces the air through the coil and through the water being sprayed over the coil.
● The heat from the refrigerant is transmitted through the metal coil to the water passing over the coil. The air removes the heat from the water by evaporating a portion of it.
● The drift eliminator (water eliminator) prevent the water droplets from being carried out with the air. The float control valve maintain a constant level of water in tank.
● As water evaporate, the level of water in tank falls down and float valve open and make up water enter in bottom tank.
● A bleed-off line is a small line leading from the pump discharge directly to the sewer.
● Since an evaporative condenser evaporates large quantity of water, remaining water becomes increasing concentration in salts and solid. If these are allowed to build up, the problem of scale formation increased.
● The bleed-off line assures that enough water will be pump to the sewer to prevent the concentration from becoming to great. .
Comparison between Air and Water Cooled Condenser:
Air cooled condenser → Water cooled Condenser
1. It is simple in construction →It is complicated in construction
2. Heat transfer capacity is less. →Heat transfer capacity is more.
3. Forced convection type condenser produce noise. →There is no noise problem.
4. Used for low capacity refrigeration plant. → These are used for high capacity plant.
5. These have no corrosion problem. →These condenser have corrosion problem.
6. There is no problem of disposal of used air. → Waste water cooled condenser have disposal problem of used water.
7. It's maintenance cost is low. → It's maintenance cost
8. Higher power consumption per TR capacity → Lower power consumption per TR capacity
9. COP lower → COP higher
10. Day night and seasonal consistency Very poor → Day night and seasonal performance consistency Very good.



 :)
:) :(
:( =(
=( ^_^
^_^ :D
:D =D
=D =)D
=)D |o|
|o| @@,
@@, ;)
;) :-bd
:-bd :-d
:-d :p
:p :ng
:ng








